Anamap Learning : Core
Everything You Need to Know About Attributes
Table of Contents
- Purpose & Definition
- Core Aspects of Attributes
- Creating Attributes
- Updating Attributes
- Deleting Attributes
- Advanced Attribute Features
- Attribute Usage
Purpose & Definition
Think of attributes like sticky notes on items in your house. Just as you might label a box "Kitchen Stuff" or "Winter Clothes", attributes in analytics are labels that tell you important details about things you're tracking.
For example:
- On a purchase: The price ($50), payment method (credit card), or shipping speed (express)
- On a user profile: Their membership level (premium), favorite color (blue), or city (Seattle)
- On a product: Its category (electronics), brand (Samsung), or status (in stock)
These labels make it easy to answer questions like "How many premium members bought electronics last month?" or "What's our average order value for express shipping?"
Core Aspects of Attributes
| Field Name | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Name | Yes | The unique identifier for the attribute within its scope |
| Scope | Yes | The context where the attribute applies (e.g., user, event) |
| Description | No | Detailed explanation of the attribute's purpose |
| Type | Yes | The basic data type for the attribute collected. Loosely corresponds with JavaScript variable types. |
| Validation Type | No | The type of validation to apply based on the Attribute type. |
| Validation | No | Specific validation rules for the attribute. |
| Origin | No | Source or system where the attribute originates. This is typically used to identify the name of data layer values the Attribute is pulled from or specific API endpoints. |
| Exposed | No | Whether the attribute is visible to ALL Anamap users instead of just Editors and Admins. If Exposed is set to false users who are Viewer will be unable to see the Attribute on Maps. |
| Nullable | No | Whether the attribute can have null values. |
Scope
Attributes can have one of three different scopes that are tightly tied to definitions used in analytics platforms and customer data platforms.
| Scope Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Event | Attributes that are scoped to an event level are not sticky. Typically these events are used for one event (or multiple on the same page/view) and then they are unset. |
| User | User level Attributes tend to be sticky. Once they are set they will apply to all future events until they are overwritten, unset, or they expire. |
| Identity | The identity scope represents Attributes that are used to identify a device as a specific user. Examples of this could be email, phone number, customer id, etc. |
Attribute Type
Attributes can be assigned one of the following data types:
| Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Text | Text values | "Premium User" |
| Integer | Whole round numeric values (integers or decimals) | 42 |
| Decimal | Numeric values that support decimals | 42.99 |
| Boolean | True/false values | true |
| Array | List of values | "red", "blue", "green" |
| JSON | Complex data structure | { "city": "Seattle", "state": "WA" } |
| DateTime | Date/time values | "2024-01-20" |
Validation Type
The validation type determines how the attribute's value should be validated. Available types include:
| Validation Type | Description | Applicable To |
|---|---|---|
| None | No validation required. For types like Boolean, Array, JSON basic validation for that type will still be used. | All types |
| Exact | Only matches the exact string entered | String |
| Enum | Validates against a list of allowed values | String |
| Regex | Validates strings against a regular expression pattern | String |
| Range | Validates numbers within a specified range | Integer or Decimal |
| JSON Schema | Validates the structure of values of JSON values | JSON |
Validation String
The validation string defines the specific rules for the chosen validation type:
| Validation Type | Format | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Exact | "string" | "match this exact string" |
| Enum | "value1,value2,value3" | "active,inactive,pending" |
| Regex | "pattern" | "^A-Za-z0-9+$" |
| Range | "min:max" | "0:100" |
| JSON Schema | JSON Schema string | {"type": "object", "properties": {"status": {"type": "string"}, "count": {"type": "integer"}}, "required": ["status"]} |
Creating Attributes
To create a new Attribute in Anamap:
- Click the "Attributes" header in the top navigation.

Attributes top nav link - In the top section of the page where it says "New Attribute", you can create a new attribute.

Create new attribute - Choose a scope (Event, User, or Identity).
- Provide a name for the Attribute.
- Select a data type (Text, Integer, Decimal, Boolean, Array, JSON, DateTime).
- Optionally choose a validation type and specify validation rules.
- Set additional fields (description, origin, exposed, nullable) as needed.
More information about the different aspects of attributes
- Click the green check mark button to save your new Attribute.
- To see it in the list you can use the Attribute Search to filter and see it. Just make sure to click the correct Scope header below the search bar that corresponds to the scope of the attribute you created.
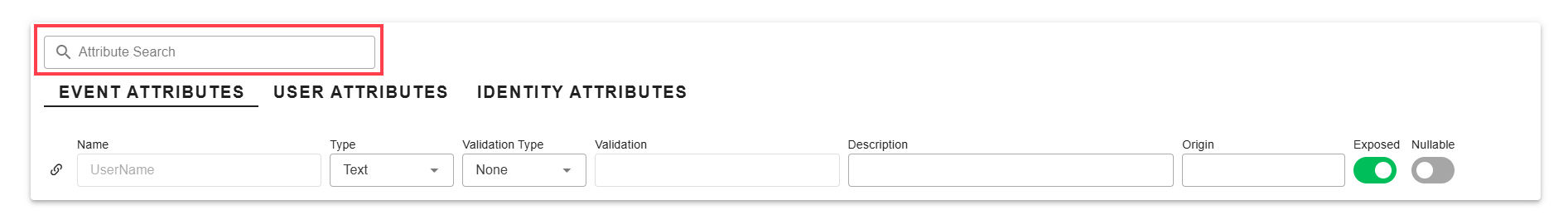
Attribute Search - Further details about the attribute can be accessed by clicking the link icon to the left of the attribute.
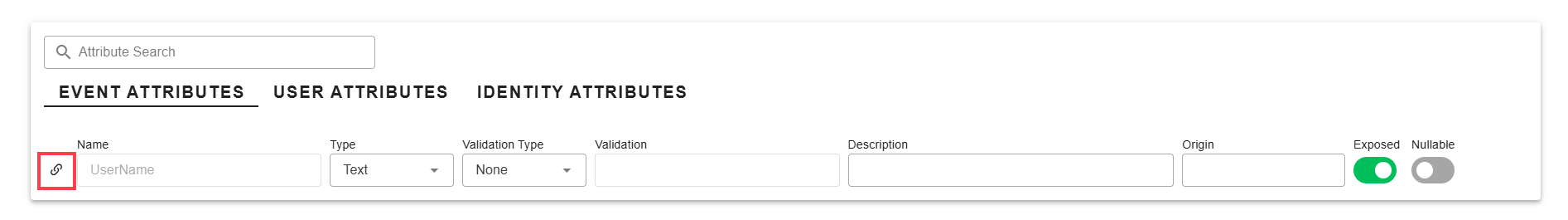
Attribute Details link
Updating Attributes
Limited aspects of an Attribute can be editted from the Attribute Index page. For most editting we recommend you dive into the Attribute Details page by clicking on the link icon next to the Attribute in the list.

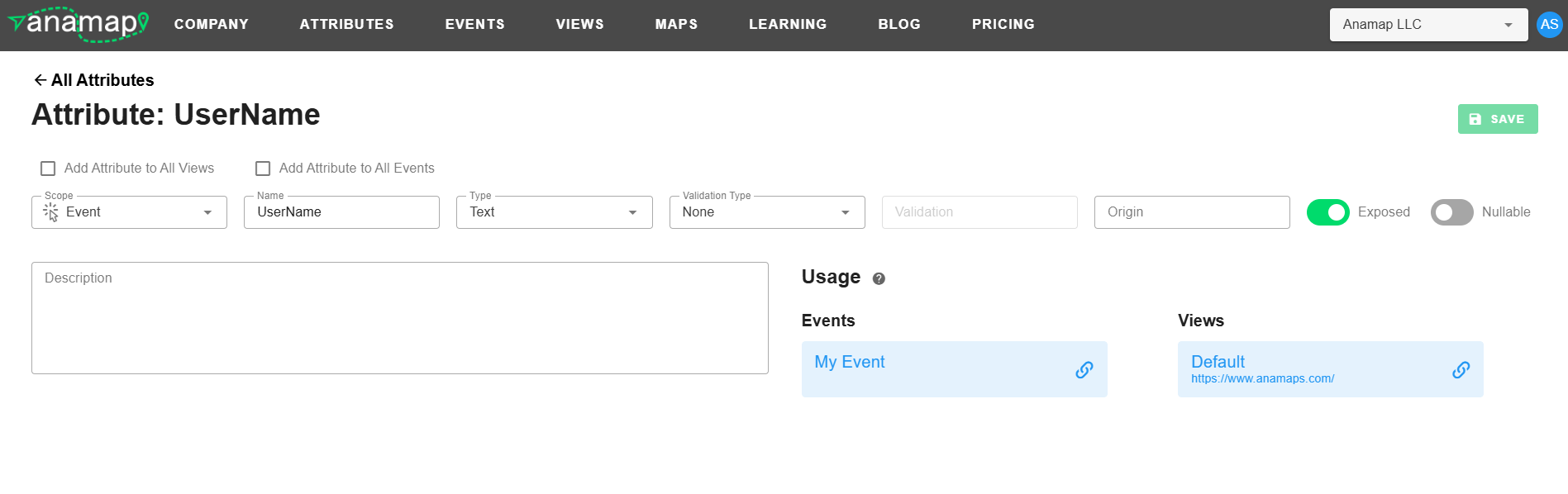
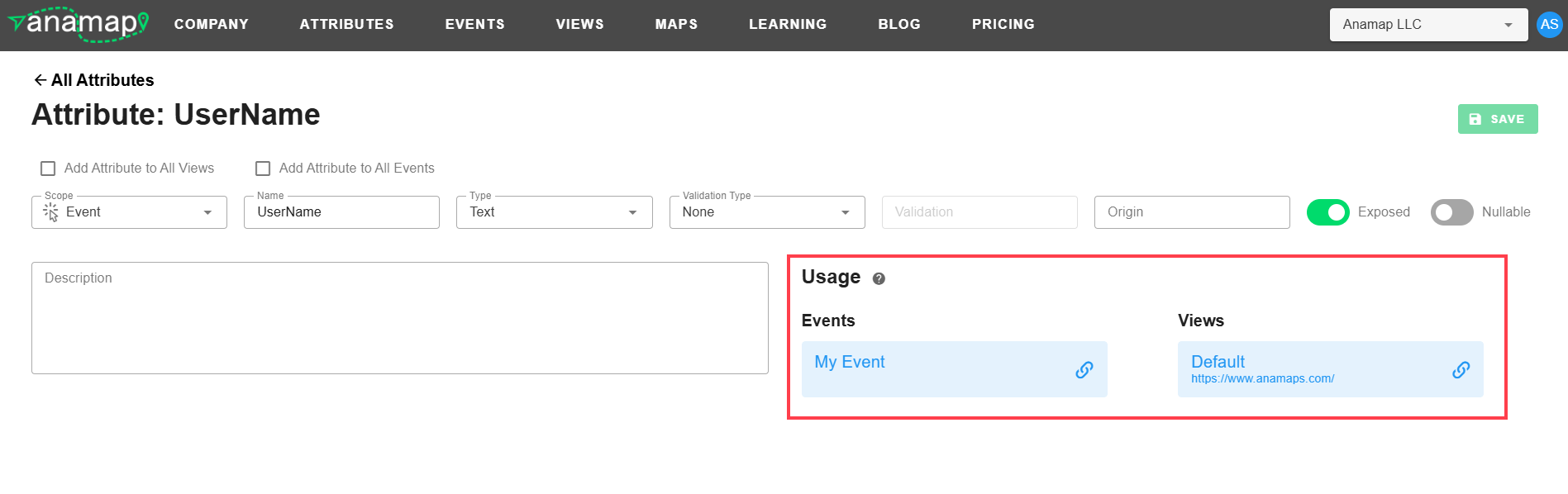
The Attribute Details page provides full access to all of the edittable aspects of an Attribute and provides some info on which Events and Views the Attribute is currently being used by.
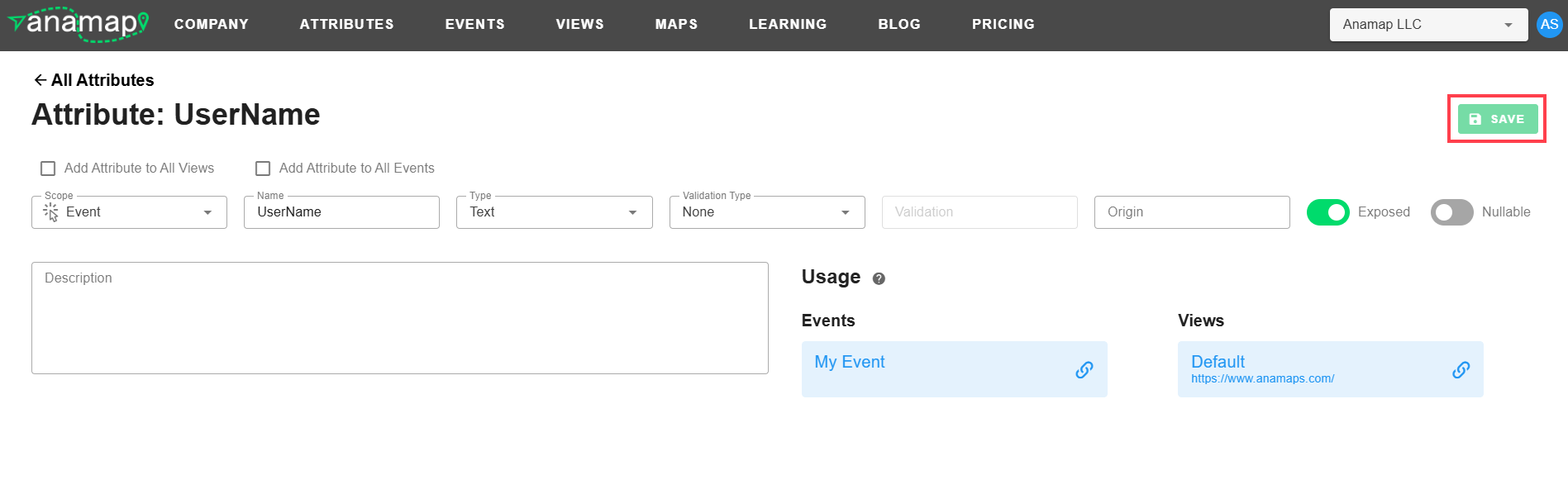
-Saving Changes: Once you've made changes to the Attribute data you can simply hit the Save button in the upper right corner of the page to save the changes. If you have a CDP sync setup the sync will automatically push your changes to the data management aspect of your CDP.
-Where the Attribute is Used: The Usage section of the Attribute Details page shows you a list of all the Events and Views that are currently utilizing the Attribute. Each of the items in the lists are linked so you can easily jump to those Events or Views if needed.
-Add Attribute to All Events or Views: For details on these checkboxes checkout the Advanced Attribute Features
Deleting Attributes
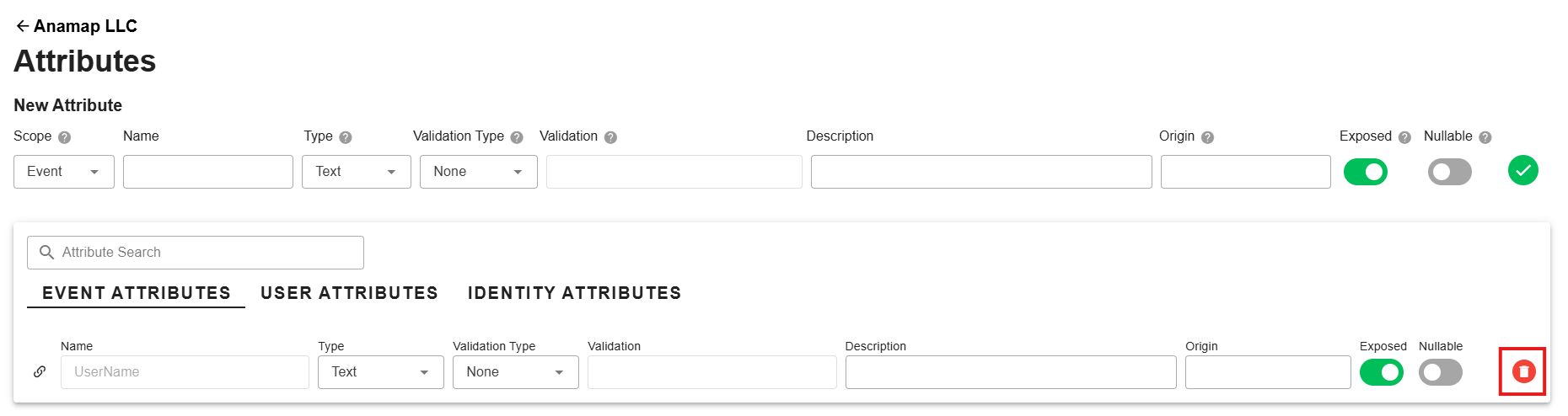
Deleting Attributes can be done from the Attribute Index page. Hover over the Attribute you'd like to delete and click the red delete button on the right side. After clicking the delete button a dialog will ask you to confirm the deletion.
Advanced Attribute Features
Add Attribute to All Views
Checking this and saving will cause the attribute to be added to all existing Views and any new Views added to your company. This is useful for attributes that are core and fundamental to nearly every View. This is typical for attributes such as the URL or domain. For specific Views that don't need the attribute you can simply delete the attribute from the View and it won't be re-added.
Add Attribute to All Events
Checking this and saving will cause the attribute to be added to all existing Events and any new Events added to your company. This is useful for attributes that are core and fundamental to nearly every event. For specific Events that don't need the attribute you can simply delete the attribute from the Event and it won't be re-added.
Attribute Usage
Attributes can be added to Events or Views. For specific information about how to add the attributes to either check out our documentation on adding attributes to Events and adding attributes to Views .